Electric vehicles are reshaping the automotive industry, and key components play a vital role. One such component is the EFB battery, or Enhanced Flooded Battery. "Understanding EFB batteries is essential for future energy solutions," says John Doe, a leading expert in battery technology. This innovative battery technology offers several advantages over traditional lead-acid batteries.
EFB batteries function on a unique principle, providing better charge acceptance and longevity. They are particularly suited for start-stop systems in modern vehicles. These batteries utilize optimized grids and innovative technology to enhance performance. However, there are still areas for improvement. EFB technology is evolving but can sometimes fall short in cold climates. The real challenge lies in achieving a balance between cost and performance.
As we delve deeper into the workings of EFB batteries, it’s clear they play a significant role in energy transition. Their potential is vast yet imperfect. The industry must continue to innovate to maximize performance while addressing existing limitations. Understanding these aspects can guide consumers and manufacturers alike in making informed decisions.

EFB batteries, or Enhanced Flooded Batteries, are an advanced type of lead-acid battery. They are designed specifically for modern vehicles with higher electrical demands. These batteries offer a blend of performance and affordability, making them popular among drivers.
One key characteristic of EFB batteries is their ability to handle deep discharge cycles. This enables them to recharge faster. They also feature a thicker positive plate, which enhances durability. Unlike traditional batteries, EFBs can withstand the demands of start-stop driving. However, they are not without flaws. Some may experience premature aging under extreme conditions.
EFBs require specific maintenance. It's important to monitor electrolyte levels regularly. While they are generally low-maintenance, neglect can lead to reduced lifespan. Users should also consider their driving habits. Frequent short trips may not fully recharge the battery. Hence, thoughtful usage is essential for optimal performance.
This chart illustrates various performance characteristics of EFB batteries, focusing on metrics such as Cold Cranking Amps (CCA), Cycle Life, Recharge Time, and Deep Discharge Recovery. The data highlights the capabilities and efficiency of EFB batteries in different applications.
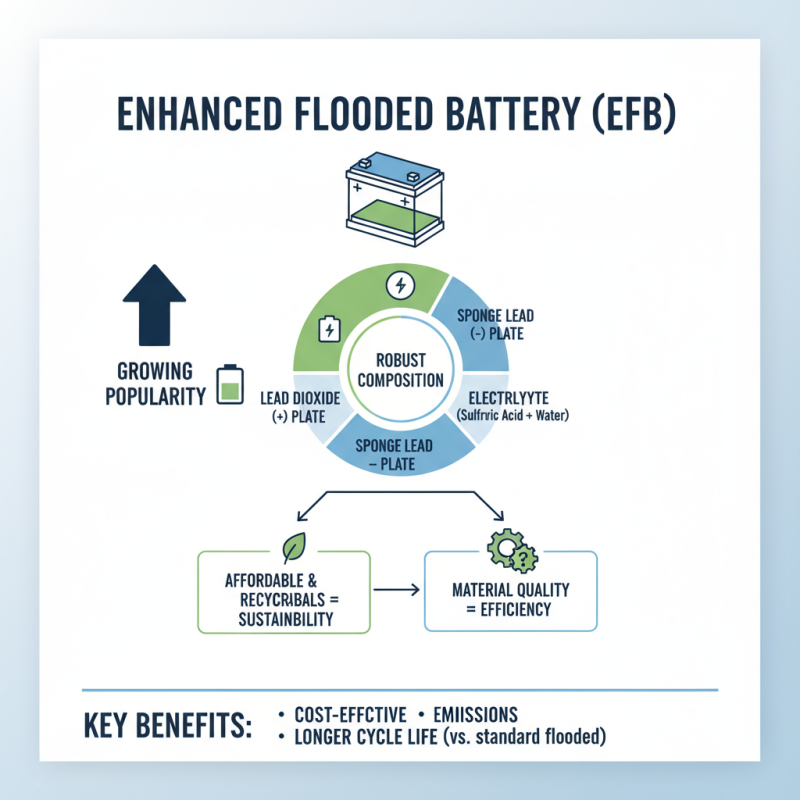
EFB batteries, or Enhanced Flooded Batteries, have become increasingly popular in various applications. Their composition plays a vital role in their performance. EFB batteries typically consist of lead dioxide, sponge lead, and electrolyte, forming a robust structure. The lead materials are affordable and recyclable, contributing to sustainability. However, their efficiency can vary based on the quality of materials used.
The technical standards for EFB batteries define their capabilities. These standards include measures for durability, charging speed, and temperature resistance. The internal construction influences the battery's life cycle and safety. Yet, some manufacturers fail to meet these standards consistently. This inconsistency can lead to problems, such as reduced performance and shorter lifespans. It's crucial to evaluate the sources of materials and adherence to technical specifications. EFB batteries demonstrate potential, but challenges remain in quality control.
EFB batteries, or Enhanced Flooded Batteries, represent a significant advancement in battery technology, particularly for automotive applications. Their construction involves thicker plates compared to standard flooded batteries, allowing for improved durability and performance. This design enables higher cycling capabilities, making them suitable for vehicles with advanced start-stop systems. A 2022 industry report revealed that EFB batteries can endure over 300 charging cycles effectively, which is a notable difference from traditional flooded batteries.
The operation of EFB batteries relies on a unique combination of electrolyte and plate design. The liquid electrolyte facilitates better ion movement during charging and discharging, boosting overall efficiency. Interestingly, EFB batteries also exhibit lower self-discharge rates. This quality is crucial in applications where vehicles may sit idle for extended periods. According to a recent study, EFB batteries experience a self-discharge rate of just 5% per month, highlighting their reliability.
Despite these advantages, EFB batteries are not without limitations. Their performance can significantly drop in extreme temperatures, rendering them less effective in harsh climates. Additionally, while their lifespan is impressive, it still may not match that of some premium battery types. This raises questions about their long-term sustainability in rapidly advancing technologies. Overall, the EFB battery is a compelling option, but users should be aware of factors that can impact its performance over time.
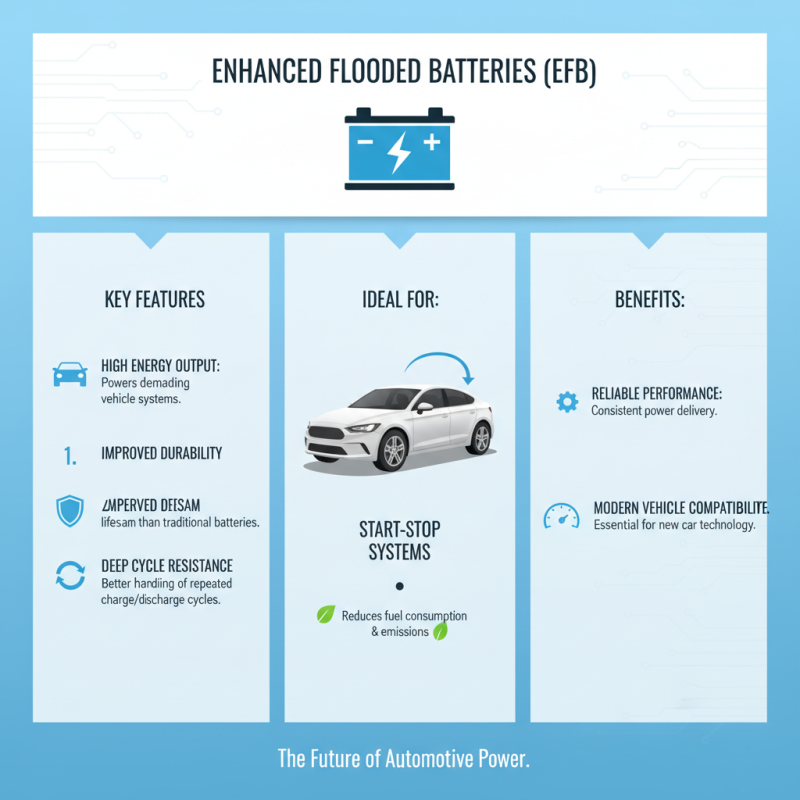
EFB batteries, or Enhanced Flooded Batteries, are gaining popularity in the automotive industry. They are designed to deliver strong performance in vehicles that demand high energy output. Unlike traditional batteries, EFB batteries have improved durability and are more resistant to the effects of deep cycling. This makes them ideal for start-stop systems used in many modern cars.
In automobiles, EFB batteries primarily serve as power sources for starting engines. They provide reliable energy for ignition and other electrical systems. Their ability to charge quickly is advantageous for vehicles that frequently stop and start, reducing wear and tear. Moreover, these batteries can handle higher temperatures, making them suitable for various climates. However, they may not be the best fit for heavy-duty applications, where deep-cycle batteries excel.
Some might question their overall lifespan. EFB batteries generally last longer than conventional options but may still require early replacement depending on usage. Regular inspections can help identify performance issues, but some drivers overlook this. The automotive industry continues to experiment with EFB technology. There are always areas for improvement and adaptation as vehicle designs evolve.
EFB batteries, or Enhanced Flooded Batteries, are designed specifically for enhanced performance. They use advanced technology to improve durability. These batteries are popular in start-stop systems found in modern vehicles. They are capable of withstanding frequent charge and discharge cycles better than traditional lead-acid batteries.
Comparing EFB and traditional lead-acid batteries reveals notable differences. EFB batteries perform well under heavy loads and have faster charging times. They also provide better energy density, usually making them a more efficient option. Traditional lead-acid batteries, while reliable, struggle with deep cycling and need longer recharge times. However, some may find EFBs pricier initially. It’s essential to weigh these factors, as not all applications are suited for EFB technology.
Installation and maintenance are other areas of concern. EFB batteries require specific setups to ensure optimal performance. In contrast, traditional lead-acid batteries can be simpler to handle. Users must consider their needs carefully. The choice between these two types of batteries can directly influence vehicle performance and longevity.